publications
Here are the previous publications I've contributed to.
2024
- Computer Vision
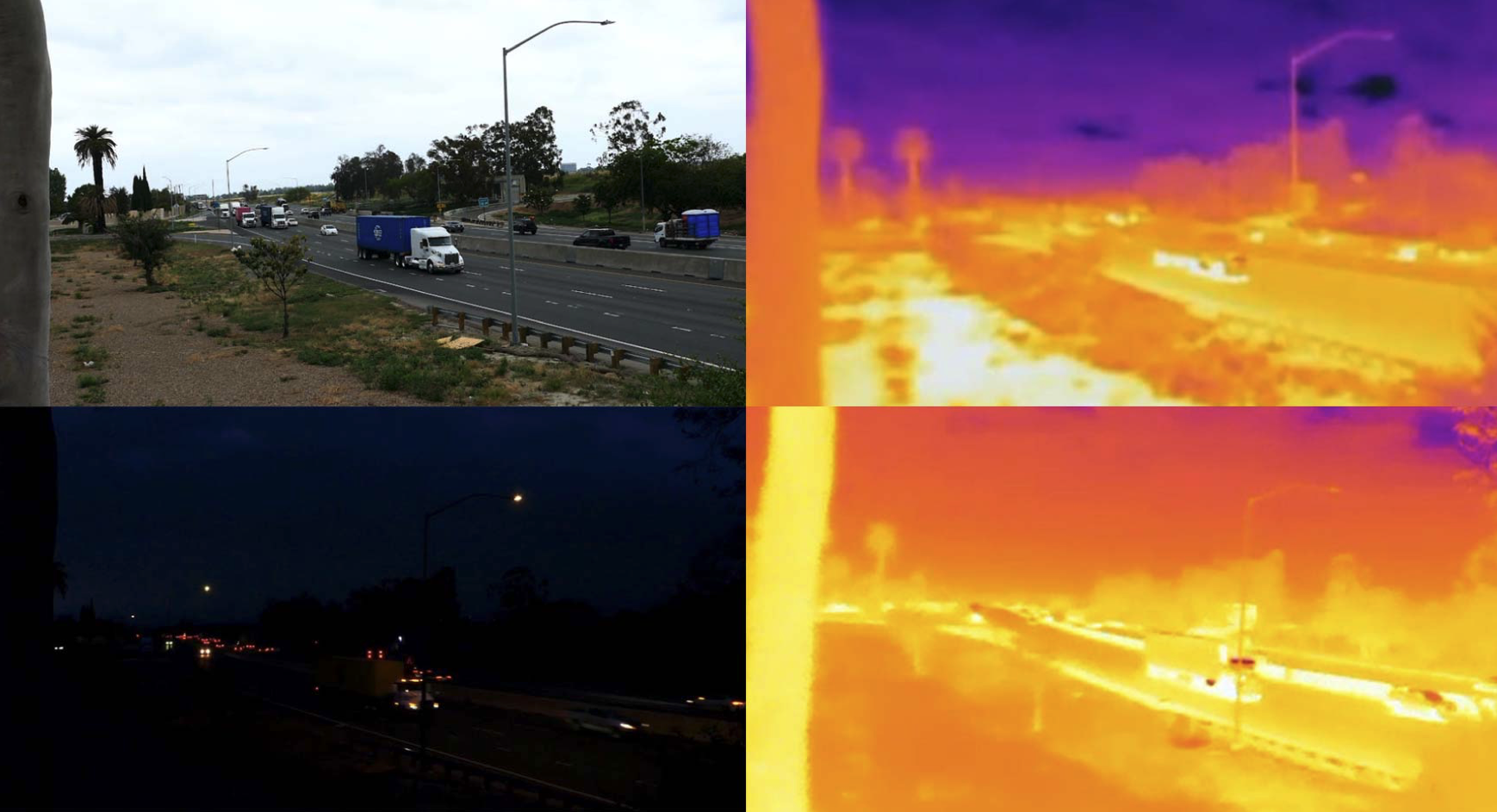 Truck Detection and Counting in Low-Light Condition: Do We Need Infrared Camera?In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp) , 2024
Truck Detection and Counting in Low-Light Condition: Do We Need Infrared Camera?In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp) , 2024Conventional visual traffic analysis methods face challenges in achieving accurate and cost-effective monitoring of truck movements, especially in adverse conditions (bad weather or nighttime). The advent of deep learning technology has revolutionized object detection such as vehicles, particularly using low-cost Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) cameras. However, object detection in low-light conditions such as nighttime is still a challenge. To address these challenges, we explore the potential of infrared imaging compared to regular imaging in truck detection and counting. Our study compares the performance of a YOLO-v5s model trained under various conditions for truck detection and counting, including day and night settings with temporally synchronized Regular and Infrared (IR) videos collected at the California 710 Freeway. Our experimental results confirmed that utilizing IR videos provides a better detection accuracy at night as expected. However, we found that just using regular videos in a specific way such as monitoring trucks at a closer distance in urban streets generates a satisfactory result which is comparable to that of IR videos. This is because there are still some lights around urban freeways even at night and hence, a regular camera is still able to successfully capture the edges of trucks. Furthermore, when the goal of monitoring truck movements is to count the number of passing trucks in a video, the accuracy of truck detection in an image is less critical than the performance of a counting algorithm.
@inproceedings{yoo2024truck, title = {Truck Detection and Counting in Low-Light Condition: Do We Need Infrared Camera?}, author = {Yoo, Jooyoung and Kim, Seon Ho and Sukhani, Krish and Yoo, Min Sang and Shahabi, Cyrus}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp)}, pages = {317--324}, year = {2024}, organization = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/BigComp60711.2024.00057}, }
2020
- Robot & Vision
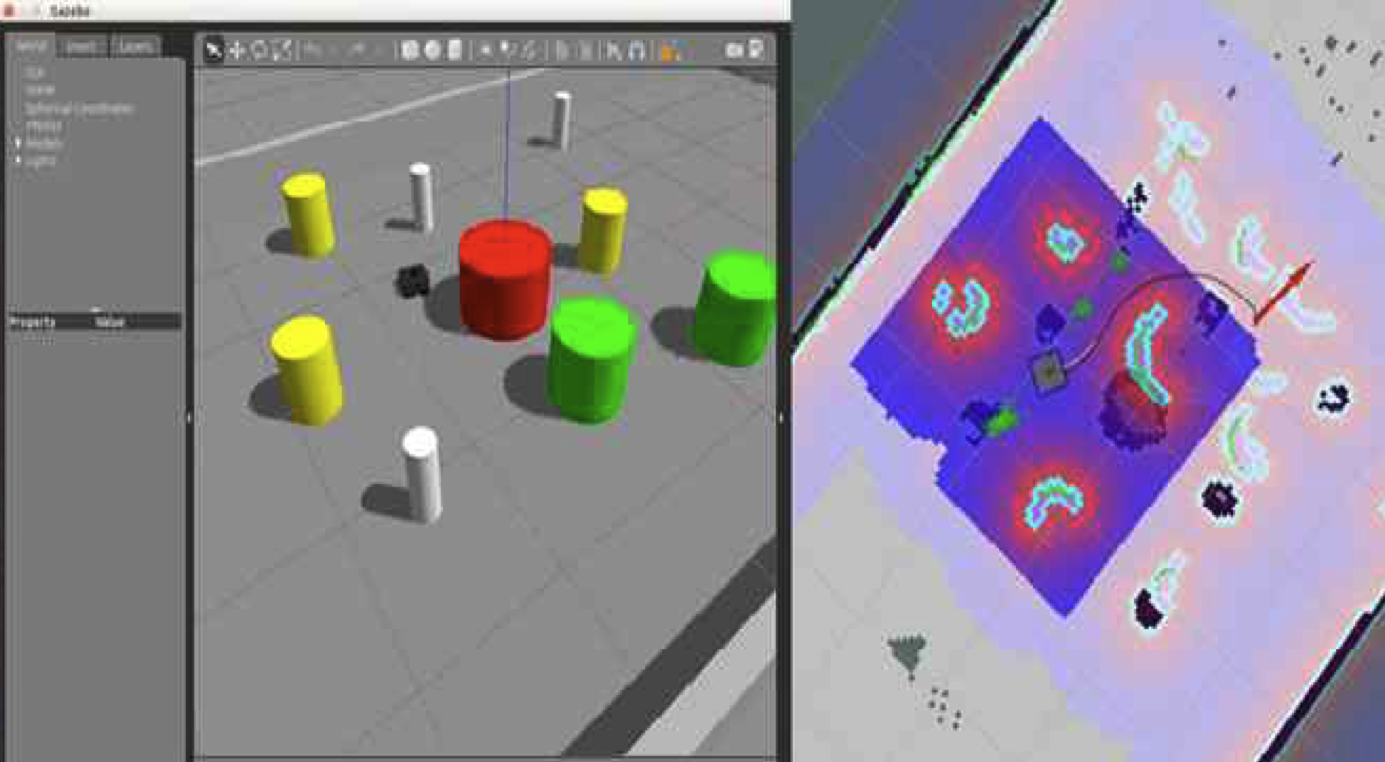 Development of a New Pedestrian Avoidance Algorithm considering a Social Distance for Social RobotsJooyoung Yoo , and Daewon KimJournal of Broadcast Engineering, 2020
Development of a New Pedestrian Avoidance Algorithm considering a Social Distance for Social RobotsJooyoung Yoo , and Daewon KimJournal of Broadcast Engineering, 2020This article proposes a new pedestrian avoidance algorithm for social robots that coexist and communicate with humans and do not induce stress caused by invasion of psychological safety distance(Social Distance). To redefine the pedestrian model, pedestrians are clustered according to the pedestrian’s gait characteristics(straightness, speed) and a social distance is defined for each pedestrian cluster. After modeling pedestrians(obstacles) with the social distances, integrated navigation algorithm is completed by applying the newly defined pedestrian model to commercial obstacle avoidance and path planning algorithms. To show the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, two commercial obstacle avoidance & path planning algorithms(the Dynamic Window Approach (DWA) algorithm and the Timed Elastic Bands (TEB) algorithm) are used. Four cases were experimented in applying and non-applying the new pedestrian model, respectively. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can significantly reduce the stress index of pedestrians without loss of traveling time.
@article{yoo2020development, title = {Development of a New Pedestrian Avoidance Algorithm considering a Social Distance for Social Robots}, author = {Yoo, Jooyoung and Kim, Daewon}, journal = {Journal of Broadcast Engineering}, volume = {25}, number = {5}, pages = {734--741}, year = {2020}, publisher = {The Korean Institute of Broadcast and Media Engineers}, doi = {10.5909/JBE.2020.25.5.734}, } - Psychology(Grit)
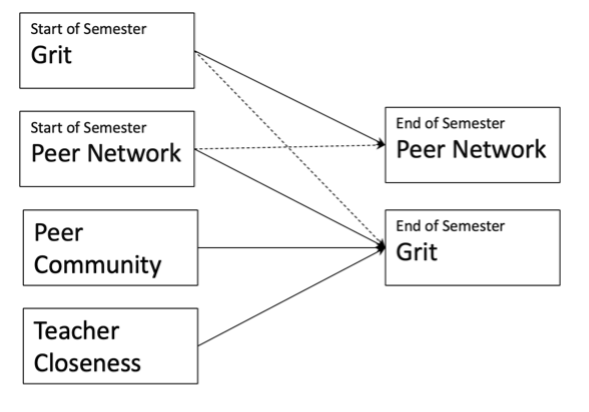 Examining the socialization of grit and the effects of peer community and teacher closeness using longitudinal social network analysisJooyoung Yoo, and Jiniee ParkThe Journal of Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction, 2020
Examining the socialization of grit and the effects of peer community and teacher closeness using longitudinal social network analysisJooyoung Yoo, and Jiniee ParkThe Journal of Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction, 2020The purpose of this study is to investigate the socialization process of grit and the effect of peer community and teacher closeness. Participants were third to sixth graders from 32 elementary school classrooms (N=963, 47.4% girls). Data was collected from the beginning and the end of the semester. Longitudinal social network analysis (SIENA) was adopted to disentangle socialization process of grit. According to the results, students select their friends based on similarity in grit (peer selection). Students with similar grit levels at the beginning of the semester tended to form cohesive peer groups at the end of the semester. Grit is more related to self-control and future-orientation based on individual student goals rather than a result of social learning. Also, peer community was found to have a positive effect on grit at the end of the semester. In contrast, teacher closeness had no significant impact. This finding indicated that peer context plays a crucial role in academic motivation and social development. The current study highlighted the peer influence on the socialization of grit and discussed the role of peers in academic adjustment.
@article{yoo2020examining, title = {Examining the socialization of grit and the effects of peer community and teacher closeness using longitudinal social network analysis}, author = {Yoo, Jooyoung and Park, Jiniee}, journal = {The Journal of Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction}, volume = {20}, number = {14}, pages = {1267--1285}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Korean Association for Learner-centered Curriculum and Instruction}, doi = {10.22251/jlcci.2020.20.14.1267}, url = {https://scholar.kyobobook.co.kr/article/detail/4010027838560}, }
2013
- Robot Algorithm
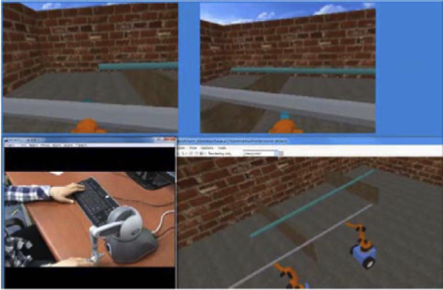 Development of a scenario-based work distribution function for tele-operation under multi-user and multi-robot environmentsJooyoung Yoo , Joomin Kim , Sungsik Yun , and Daewon KimIn IEEE ISR 2013 , 2013
Development of a scenario-based work distribution function for tele-operation under multi-user and multi-robot environmentsJooyoung Yoo , Joomin Kim , Sungsik Yun , and Daewon KimIn IEEE ISR 2013 , 2013In this paper, the development of a scenario based work distribution function for tele-operation under multi-user and multi-robot environments is described. First of all, XML-based UDS(Unit-task Description Structure) is defined to make task scenarios, to distribute the work to multi-users and to consider emergency states in the task. Considering the role of users and control methods, various kinds of switching modes are defined, and a switching controller is designed. To prove the work distribution function, a simulation environment including a Marilou robotic simulator based slave robot environment is implemented. In this environment, the effectiveness of the work distribution function is tested.
@inproceedings{yoo2013development, title = {Development of a scenario-based work distribution function for tele-operation under multi-user and multi-robot environments}, author = {Yoo, Jooyoung and Kim, Joomin and Yun, Sungsik and Kim, Daewon}, booktitle = {IEEE ISR 2013}, pages = {1--3}, year = {2013}, organization = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/ISR.2013.6695631}, }